5. How to set electrode reduction
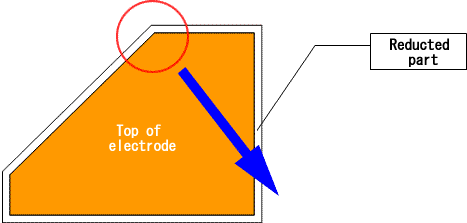
EDM is a machining method to transfer the shape of the electrode to the workpiece, and the shape of electrodes must be smaller than the objective machining shape. This amount to be reduced is called "electrode reduction amount". "Electrode reduction amount " is around 0.03-2.0mm, and it varies according to EDM conditions to use, and so on. Here, we explain how to reduce the dimensions of the electrode shape.
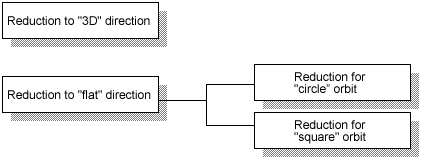
Methods of the electrode reduction are distinguished mainly between reduction to "flat" direction and reduction to "3D" direction.
"Reduction to '3D' direction" is a method to reduce to the normal direction for all surfaces. This is the most common method of reduction for electrodes designed by 3D CAD. "Sphere" orbit is used at EDM.
"Reduction to 'flat' direction" is a method to reduce to two-dimensional directions. It is a method used for electrodes of the two-dimensional shape and is generally used for electrodes for precision molds. "Circle" orbit and "square" orbit which are flat orbits are used. Particularly, "square" orbit is used when a sharp corner shape is required. "Square" orbit is mainly used for rectangular shape electrodes. But when the electrode has a non-rectangular shape part also, special design is necessary to prevent a shape error at EDM.
Each of "reduction to 'flat' direction" and "reduction to '3D' direction”has advantages and disadvantages. It is necessary to have a good command of them by the machining purpose.
1) Reduction to '3D' direction
<Reduction method>
- Reduce to the normal direction for all surfaces
<Advantages>
- Reduced shape can be automatically designed by 3D CAD.
- Reduction is easily made by changing the diameter of the ball end mill at processing electrodes.
<Disadvantages>
- An R part depending on the reduction amount occurs in the corner part of the shape.
- Encroachment occurs at EDM except with "sphere" orbit.
- Machining efficiency is poor because of using "sphere" orbit at EDM.
<Molds applied>
It is used in general molds.
When the demand of machining accuracy is not severe, "flat" orbit, which has high machining efficiency by ignoring encroachment, may be used instead of "sphere" orbit which is inefficient at EDM.
(1)An example of "reduction for '3D' direction" and movement of "sphere" orbit
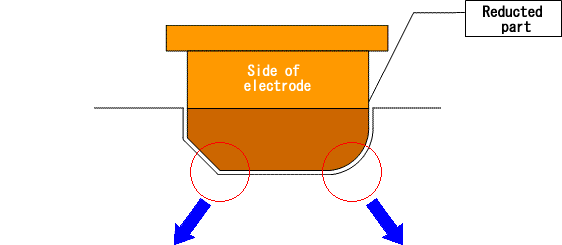
Because R-shaped leftover equivalent to the
reduction amount occurs at the part of the
electrode bottom, it is impossible to make the
reduction amount large for finish electrodes.
Put the mouse onto the image to see an animation.
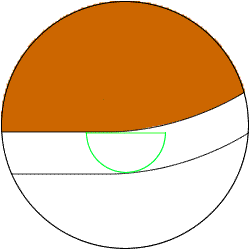
The R part of the electrode bottom is
transferred to the correct shape.
Put the mouse onto the image to see an animation.
(2)Movement and encroaching part by using "flat" orbit instead of "sphere" orbit
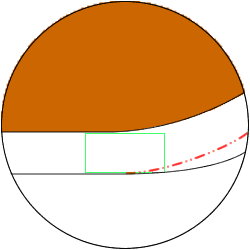
Flat orbit encroaches into the corner part of electrode bottom, and it machines beyond the red line
which is the correct machining shape. Put the mouse onto the image to see an animation.
2) Reduction to 'flat' direction
<Reduction method>
- Reduce into the shape that offset inward for the shape in the two-dimensional flat surface.
- The C surface and R part of the bottom corner part are set as the same dimensions and aren't reduced.
- When you use square orbit in non-rectangular shape, special reduction method is necessary.
<Advantage>
- Sharp corners on the bottom can be transcribed at EDM.
<Disadvantage>
- It is difficult to design a 3D shape electrode.
<Molds applied>
Used for precision molds. Generally, as for the precision molds, there are many cases that sharp edge of the corner part is required.
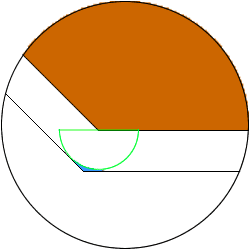
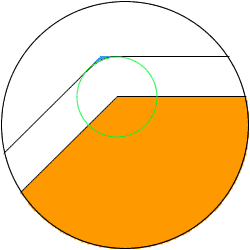
(1) Movement of "circle” orbit
Because R-shaped leftover equivalent to the
reduction amount occurs at the corner part by
"circle" orbit, it is impossible to make the
reduction amount large for finish electrodes.
Put the mouse onto the image to see an animation.
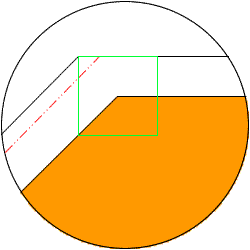
(2)The movement and encroached part of "square" orbit with a non-rectangular electrode
"Square" orbit encroaches into the corner
part of the electrode, and it processes beyond
the red line which is the correct machining
shape.
Put the mouse onto the image to see an animation.
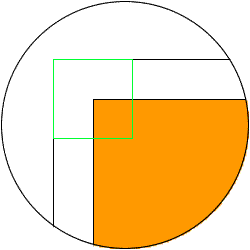
(3) A rectangular shape electrode and the movement of "square" orbit
The corner part is sharply machined by
"square" orbit.
Put the mouse onto the image to see an animation.
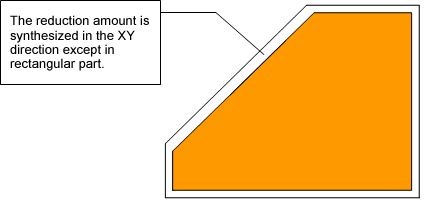
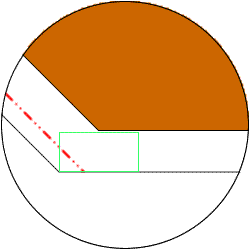
(4)Reduction method of using "square" orbit in non-rectangular electrodes
In EDM of precision molds, "square" orbit is used for rectangular electrodes to process corners sharply. However, encroachment occurs partly if using "square" orbit when the electrode is not a complete rectangle. Reduction method of EDM for a non-rectangular shape with "square" orbit is different from that with "circle" orbit, and it must be reduced to the X/Y axial direction as reduction for "square" orbit.
As shown below, the corners must be reduced larger than other parts, and electrode design becomes difficult when the shape is complicated. (In the example below, the reduction amount of the 45 degree slope part becomes the amount synthesized in the XY direction in comparison with other parts, and it is multiplied by square root of 2.)